Hello! 👋
Today we continue exploring AI capabilities in .NET.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) capabilities have become essential in modern applications. However, leveraging AI often involves cloud-based APIs, which can be limited by connectivity and recurring costs. For developers building applications with .NET MAUI, LLamaSharp offers an excellent solution for running AI models locally, without requiring an internet connection. By integrating LLamaSharp, developers can achieve efficient offline execution of large language models (LLMs).
This article provides a step-by-step guide to integrating LLamaSharp into your .NET MAUI application.
What is LLamaSharp?
LLamaSharp is a .NET wrapper around LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI), enabling the execution of LLaMA models in .NET applications. With LLamaSharp, developers can perform inference directly on the user's device, avoiding the need for cloud-based AI services.
Setting Up Your .NET MAUI Application with LLamaSharp
Step 1: Install LLamaSharp NuGet Package
Open your .NET MAUI project and install the LLamaSharp NuGet packages and one or more of these backends depending on your target device:
LLamaSharp.Backend.Cpu: Pure CPU for Windows, Linux & Mac. Metal (GPU) support for Mac.
LLamaSharp.Backend.Cuda11: CUDA 11 for Windows & Linux.
LLamaSharp.Backend.Cuda12: CUDA 12 for Windows & Linux.
LLamaSharp.Backend.Vulkan: Vulkan for Windows & Linux.
My configuration for Windows with Vulkan backend:
Step 2: Prepare Your LLaMA Model
Download a compatible LLaMA model from Ollama or another source. Ensure that the model is in a format supported by LLamaSharp. Save the model file in your application's resources or a known path.
There are two popular formats of model files of LLMs, these are PyTorch format (.pth) and Huggingface format (.bin). LLamaSharp uses a GGUF format file, which can be converted from these two formats. To get a GGUF file, search model name + 'gguf' in Huggingface.
I downloaded the Llama 3.1 model (Link).
Step 3: Integrate LLamaSharp into Your .NET MAUI Project
Create a service for loading and running the LLaMA model:
For my sample app I received the next output:
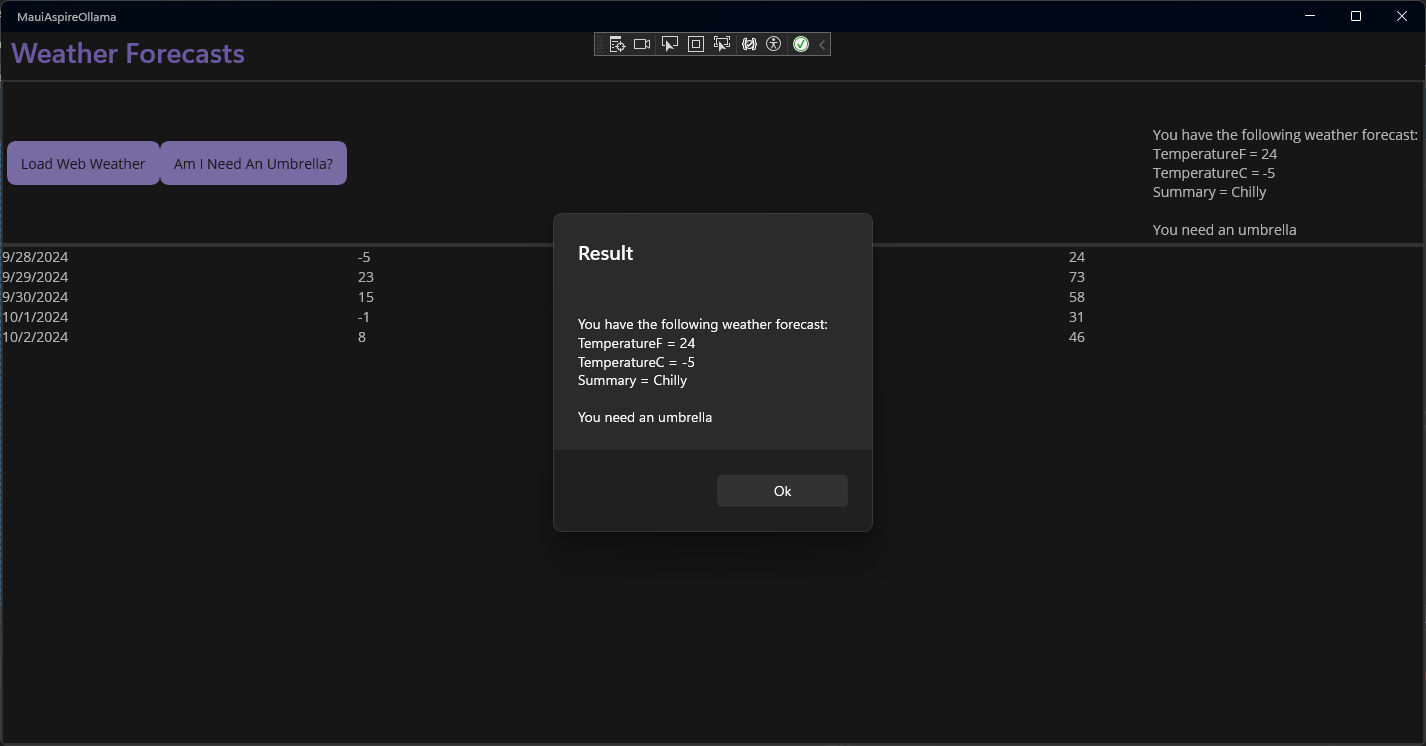
Step 4: Optimize for Device Performance
Running large models locally can be resource-intensive. To ensure smooth performance:
Reduce Model Size: Use smaller versions of LLaMA models, such as LLaMA-3B or quantized variants.
Adjust Context Size: Configure the context size to balance performance and output quality.
Test on Target Devices: Test your application on actual devices, particularly lower-powered ones.
Conclusion
With LLamaSharp, .NET MAUI developers can incorporate cutting-edge AI into their applications without relying on internet connectivity or incurring cloud costs. This approach is ideal for privacy-focused, offline, or internal-use apps.
Start exploring the potential of offline AI today and take your .NET MAUI applications to the next level!
The full code can be found on GitHub.

