Hello!
If you feel alone and are looking for someone for a coffee talk, maybe that someone is in front of you. Yes, it is your device. ;-) Imagine, that you ask your device a question and it replies to you. This article is devoted to a built-in speech recognition mechanism.
.NET MAUI already has a mechanism to convert text to speech. There is a method SpeakAsync, that receives a text you want to hear:
Let's create a similar API, but for Speech-To-Text.
Starting from the interface:
where culture is our spoken language, recognitionResult is an intermediate response from the Recognizer, cancallationToken is used for stopping the process. The result of the method returns the final string output from the Recognizer.
Android
Speech recognizer requires access to a microphone and the Internet, so add these lines to AndroidManifest.xml:
Now let's implement our ISpeechToText interface:
The main 2 lines here are:
The first line set the SpeechRecognitionListener that has a list of methods for different states of your speech recognition.
The second line creates speech intent, which has a configuration for speech recognizer and then starts the listening.
iOS/MacCatalyst
Speech recognizer requires access to a microphone, so add these lines to Info.plist:
Now let's implement our ISpeechToText interface:
Similar to Android here we also create SpeechRecognizer and configure AudioEngine. By analogy with SpeechRecognitionListener Apple has a method speechRecognizer.GetRecognitionTask where the second Action parameter contains recognition results.
Windows
Speech recognizer requires access to a microphone and the Internet (In case you choose online recognition), so add these lines to the Capabilities in Package.appxmanifest:
The same as with Android and iOS we implement ISpeechToText interface:
Sample
And the most pleasant step to check that everything works:
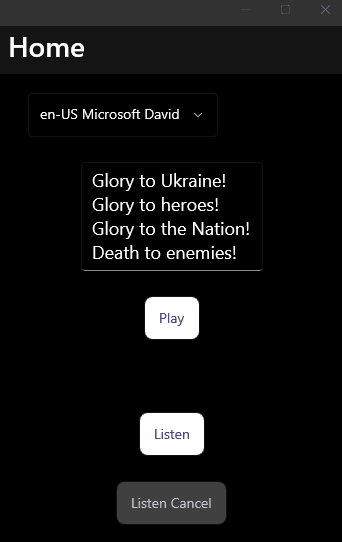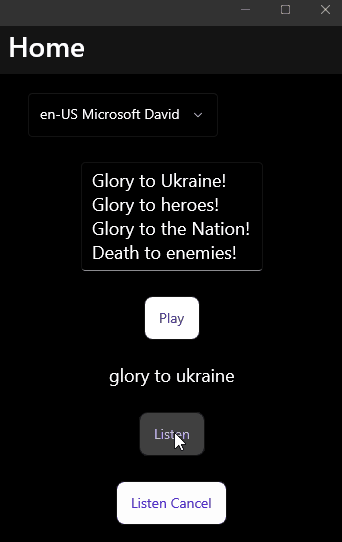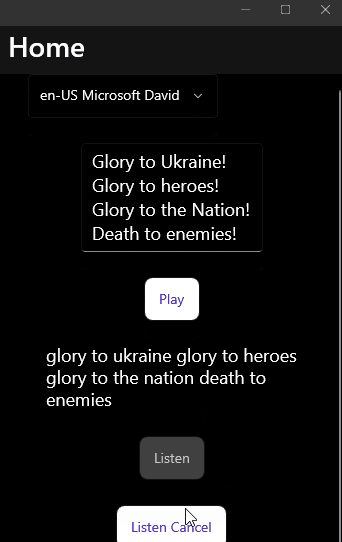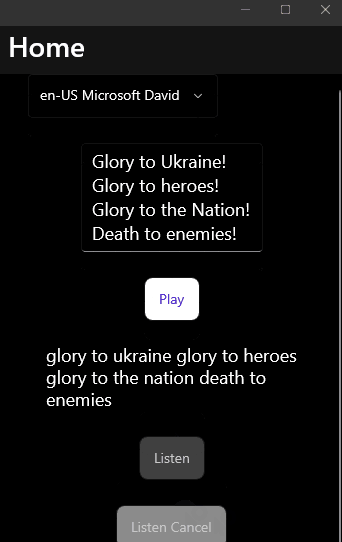
The final code can be found on GitHub.
Happy coding and never be alone!